Perceptrons
A Perceptron is an Artificial Neuron
It is the simplest possible Neural Network
Neural Networks are the building blocks of Machine Learning.
Frank Rosenblatt
Frank Rosenblatt (1928 – 1971) was an American psychologist notable in the field of Artificial Intelligence.
In 1957 he started something really big. He "invented" a Perceptron program, on an IBM 704 computer at Cornell Aeronautical Laboratory.
Scientists had discovered that brain cells (Neurons) receive input from our senses by electrical signals.
The Neurons, then again, use electrical signals to store information, and to make decisions based on previous input.
Frank had the idea that Perceptrons could simulate brain principles, with the ability to learn and make decisions.
The Perceptron
The original Perceptron was designed to take a number of binary inputs, and produce one binary output (0 or 1).
The idea was to use different weights to represent the importance of each input, and that the sum of the values should be greater than a threshold value before making a decision like true or false (0 or 1).
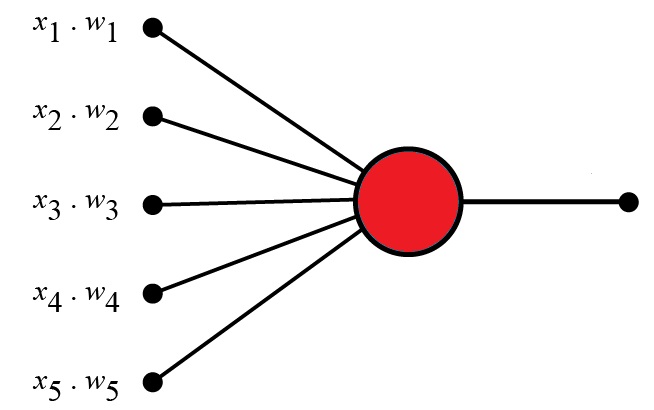
Perceptron Example
Imagine a perceptron (in your brain).
The perceptron tries to decide if you should go to a concert.
Is the artist good? Is the weather good?
What weights should these facts have?
| Criteria | Input | Weight |
|---|---|---|
| Artists is Good | x1 = 0 or 1 | w1 = 0.7 |
| Weather is Good | x2 = 0 or 1 | w2 = 0.6 |
| Friend will Come | x3 = 0 or 1 | w3 = 0.5 |
| Food is Served | x4 = 0 or 1 | w4 = 0.3 |
| Alcohol is Served | x5 = 0 or 1 | w5 = 0.4 |
The Perceptron Algorithm
Frank Rosenblatt suggested this algorithm:
- Set a threshold value
- Multiply all inputs with its weights
- Sum all the results
- Activate the output
1. Set a threshold value:
- Threshold = 1.5
2. Multiply all inputs with its weights:
- x1 * w1 = 1 * 0.7 = 0.7
- x2 * w2 = 0 * 0.6 = 0
- x3 * w3 = 1 * 0.5 = 0.5
- x4 * w4 = 0 * 0.3 = 0
- x5 * w5 = 1 * 0.4 = 0.4
3. Sum all the results:
- 0.7 + 0 + 0.5 + 0 + 0.4 = 1.6 (The Weighted Sum)
4. Activate the Output:
- Return true if the sum > 1.5 ("Yes I will go to the Concert")
Note
If the weather weight is 0.6 for you, it might different for someone else. A higher weight means that the weather is more important to them.
If the threshold value is 1.5 for you, it might be different for someone else. A lower threshold means they are more wanting to go to the concert.
Example
const threshold = 1.5;
const inputs = [1, 0, 1, 0, 1];
const weights = [0.7, 0.6, 0.5, 0.3, 0.4];
let sum = 0;
for (let i = 0; i < inputs.length; i++) {
sum += inputs[i] * weights[i];
}
const activate = (sum > 1.5);
Perceptron Terminology
- Perceptron Inputs
- Node values
- Node Weights
- Activation Function
Perceptron Inputs
Perceptron inputs are called nodes.
The nodes have both a value and a weight.
Node Values
In the example above, the node values are: 1, 0, 1, 0, 1
The binary input values (0 or 1) can be interpreted as (no or yes) or (false or true).
Node Weights
Weights shows the strength of each node.
In the example above, the node weights are: 0.7, 0.6, 0.5, 0.3, 0.4
The Activation Function
The activation functions maps the result (the weighted sum) into a required value like 0 or 1.
In the example above, the activation function is simple: (sum > 1.5)
The binary output (1 or 0) can be interpreted as (yes or no) or (true or false).
Note
It is obvious that a decision is NOT made by one neuron alone.
Other neurons must provide input: Is the artist good. Is the weather good...
In Neuroscience, there is a debate if single-neuron encoding or distributed encoding is most relevant for understanding brain functions.
Neural Networks
The Perceptron defines the first step into Neural Networks.
Multi-Layer Perceptrons can be used for very sophisticated decision making.
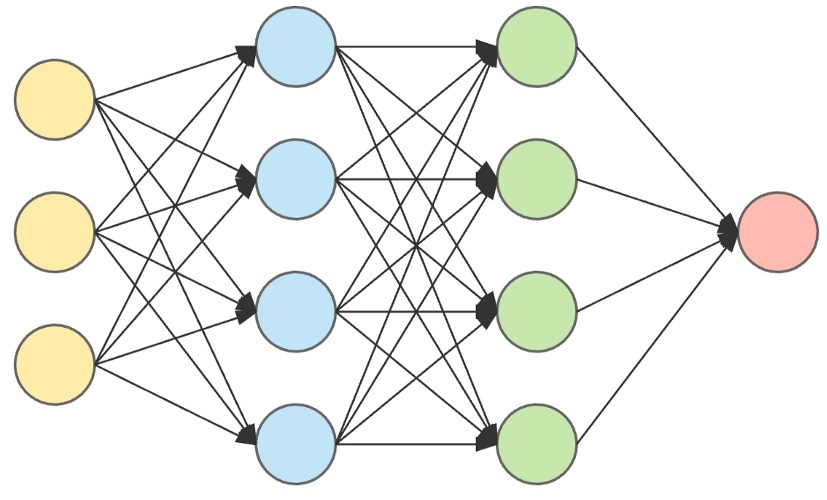
In the Neural Network Model, input data (yellow) are processed against a hidden layer (blue) and modified against more hidden layers (green) to produce the final output (red).
The First Layer:
The 3 yellow perceptrons are making 3 simple decisions based on the input evidence.
Each single decision is sent to the 4 perceptrons in the next layer.
The Second Layer:
The blue perceptrons are making decisions by weighing
the results from the first layer. This layer make more complex decisions
at a more abstract level than the first layer.
The Third Layer:
Even more complex decisions are made by the green perceptons.


