AWS Cloud Containers
Containers in the AWS Cloud
Containers are popular for deploying and managing applications in the cloud.
Containers let you package code in a single object.
The container isolates the code and removes the dependencies to other components.
It runs in isolation.
Containers are an essential concept in micro service architectures.
Containerized Approach
Having the application in a container makes debugging easier.
It makes it easier because the application is inside of an isolated container.
The container remains consistent regardless of deployment.
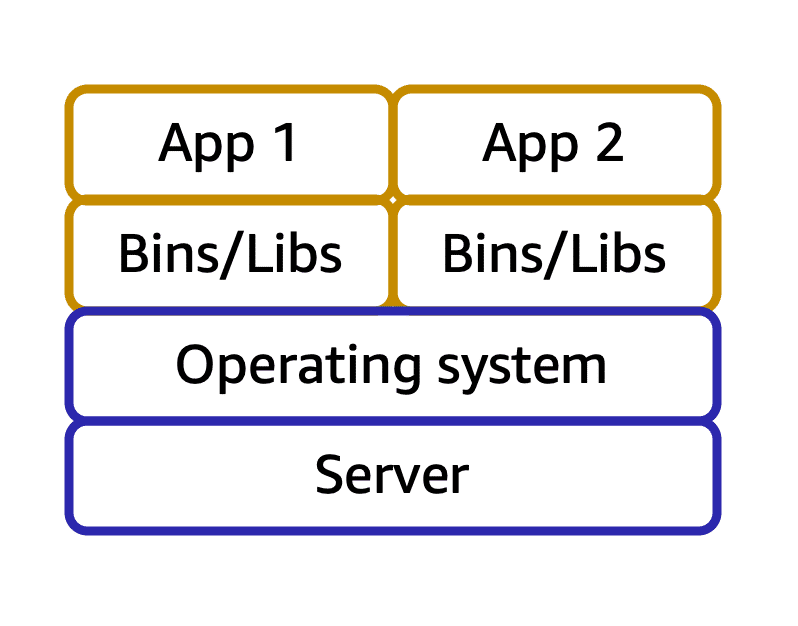
Image created by Amazon Web Services
The picture illustrates one host with containers.
Containers and Scale
It is important to design for scale when using containers.
There could be tens of hosts with hundreds of containers as the environment grows.
One should prepare for how to manage operations at scale.
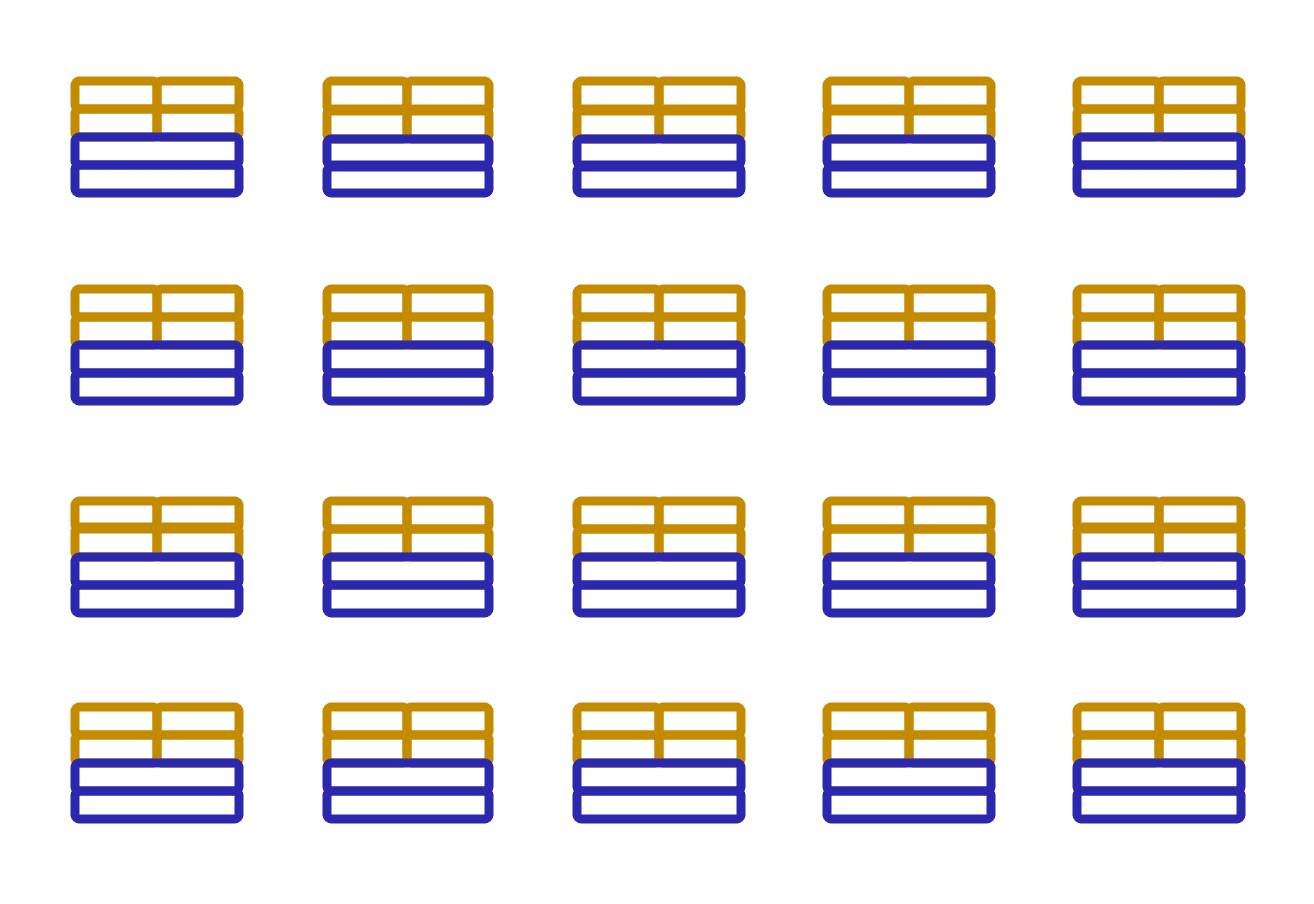
Image created by Amazon Web Services
This picture illustrates containers in a scaled environment.
Container orchestration services help you deploy, manage, and scale your containerized applications.
In the following chapters, you will learn about two services that provide container orchestration: AWS Elastic Container Service and AWS Elastic Kubernetes Service.
AWS Cloud Exercises
Relevant Specializations and Guided Projects
- Deploy Wordpress Site EC2
- MySQL DB with AWS RDS
- Website Hosting and Replication
- Create Amazon Aurora DB
- AWS Elastic Container Registry


