AWS Instance Stores
What are Instance Stores?
Instance Store is a storage volume that acts as a physical hard drive.
It provides temporary storage for Amazon EC2 instance.
The data in an instance store persists during the lifetime of its instance.
If an instance reboots, data in the instance store will persist.
When the instance hibernates or terminates, you lose any data in the instance store.
If an instance starts from a stopped state, it might start on another host where the used instance store does not exist.
It is recommended to avoid storing valuable data in the store instance.
Instance Stores are good for temporary files, and data that can be easily recreated.
AWS Instance Stores and AWS EBS Video
W3schools.com collaborates with Amazon Web Services to deliver digital training content to our students.
You will learn about AWS EBS in the next chapter.
Example:
AWS EC2 instance with an attached instance store is running.
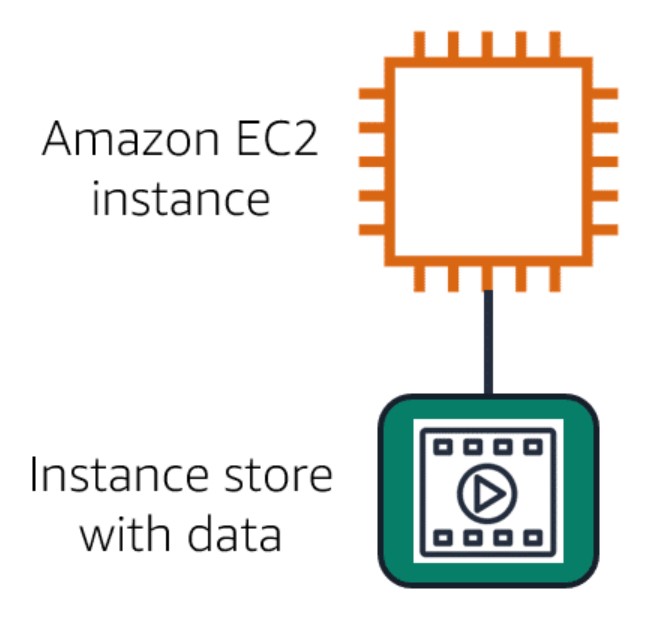
Image created by Amazon Web Services
AWS EC2 instance is stopped or terminated.
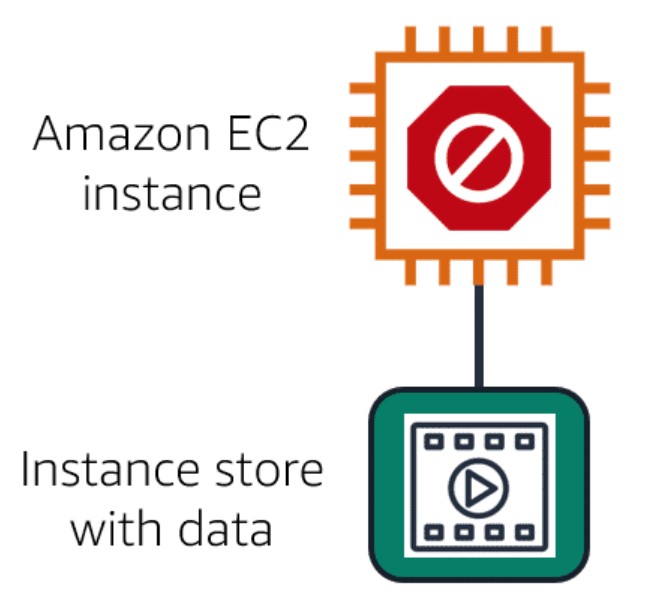
Image created by Amazon Web Services
All data on the attached instance store are deleted.
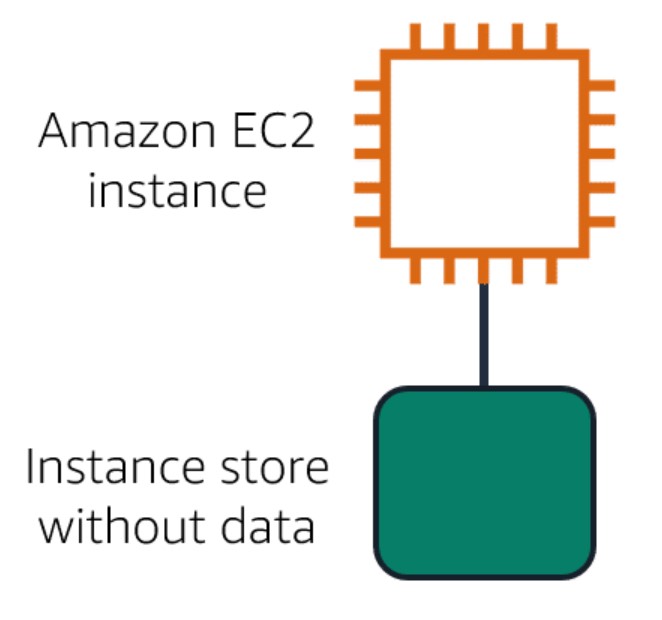
Image created by Amazon Web Services


