User Permissions and Access
What is AWS Identity and Access Management?
AWS IAM is also called AWS Identity and Access Management.
It helps you securely manage AWS resources and services.
IAM features are:
- AWS account root user
- IAM Users
- IAM policy
- IAM groups
- IAM roles
- Multi-factor authentication
By combining IAM features, you have the flexibility to configure specific operational and security access.
User Permissions and Access Video
W3schools.com collaborates with Amazon Web Services to deliver digital training content to our students.
AWS Account Root User
AWS account root user gets created when you first start an AWS account.
Access your account root user by AWS account credentials (email and password).
It has full access to all of the accounts resources and AWS services.
Some of the good practices are:
- Avoid using the root user for daily tasks
- Use it to create IAM with permissions to create other users
- Use it only for the root user-specific tasks
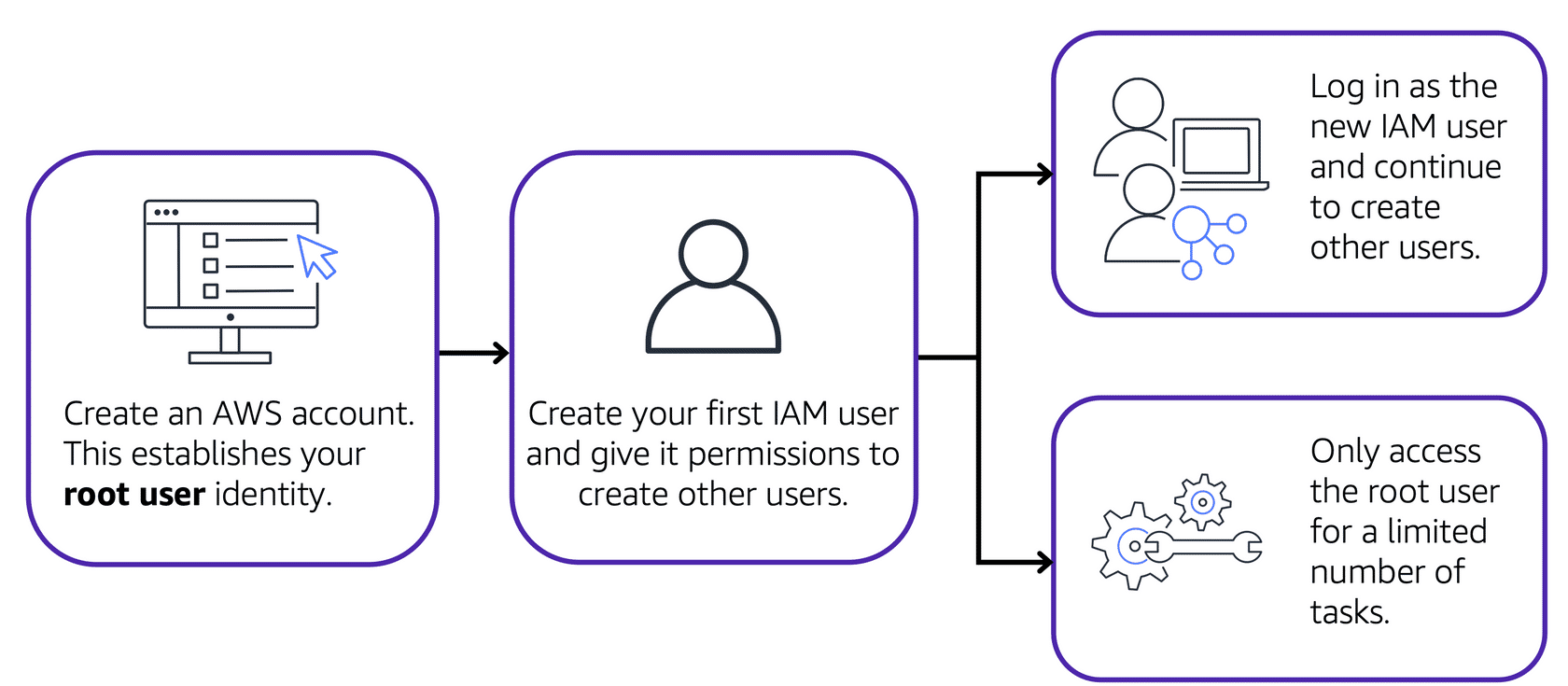
Image created by Amazon Web Services
IAM Users
IAM user represents an entity (person or an application) that interacts with AWS resources and services.
IAM user is made of credentials and a name.
It is created without permissions by default.
The root user can grant permissions to the IAM user.
It is recommended that you create one IAM user for each individual.
IAM Policies
IAM policies are documents.
They deny or allow permissions to AWS resources and services.
They customize user access to AWS resources and services.
You can give only those permissions that each user needs.
IAM policy example is illustrated below.

Image created by Amazon Web Services
IAM Groups
A collection of IAM users is called an IAM group.
IAM policy assigned to the IAM group grants permissions to all IAM users of that group.
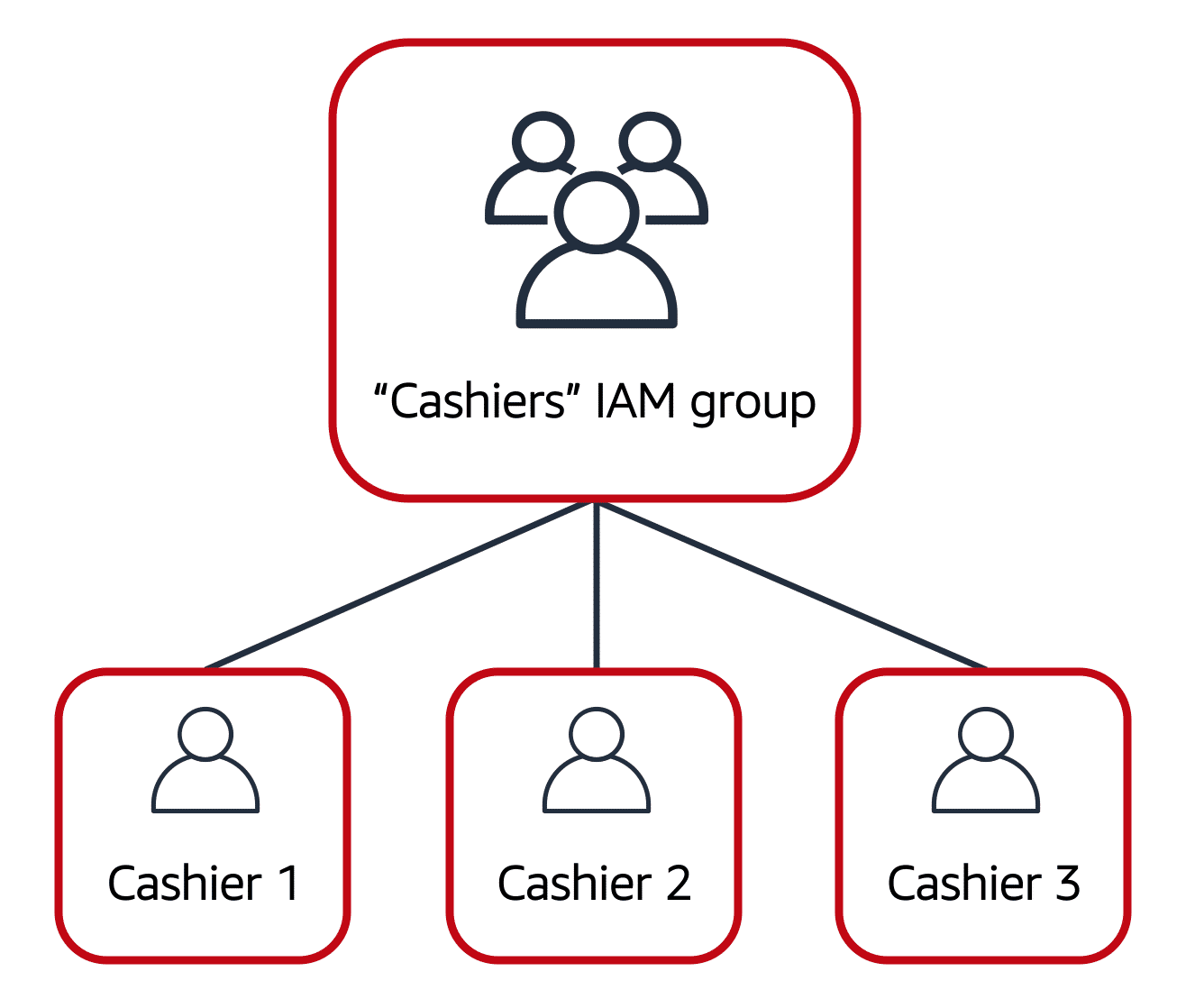
Image created by Amazon Web Services
IAM Roles
IAM role is temporary access to services or resources.
Before an IAM role can be given, IAM user, service, or application must have permission to switch roles.
It is best for cases where temporary access needs to be given.
Multi-factor Authentication
Multi-factor authentication is a multiple-step authentication.
It can provide more than one authentication form.
It is an extra layer of security.
It may come in the form of a security code that is sent to your mobile device or an email.


