AWS Cloud Global Networking
Global Networking Video
W3schools.com collaborates with Amazon Web Services to deliver digital training content to our students.
Domain Name System
Domain Name System is also called DNS.
DNS is the service that lets someone access your website from their browser.
The DNS is like a phone book.
It connects the IP address to the domain name.
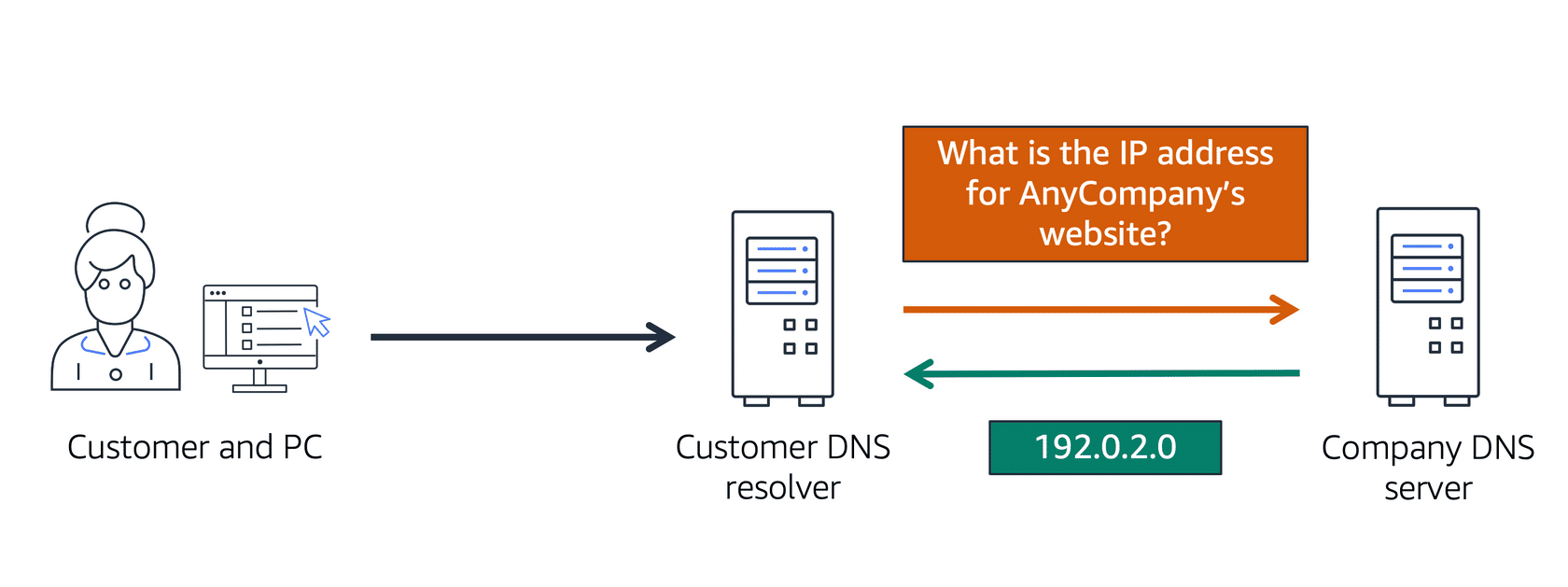
Image created by Amazon Web Services
AWS Route 53
Route 53 is a DNS web service.
It routes end users to internet apps hosted in AWS.
Route 53 connects users and their requests to AWS resources and external resources.
Route 53 has a feature to manage DNS records.
You can register new and transfer domains with Route 53.
You can manage all of your domain names from Route 53.
Use AWS Route 53 and AWS CloudFront
Route 53 and CloudFront can be combined to deliver content.
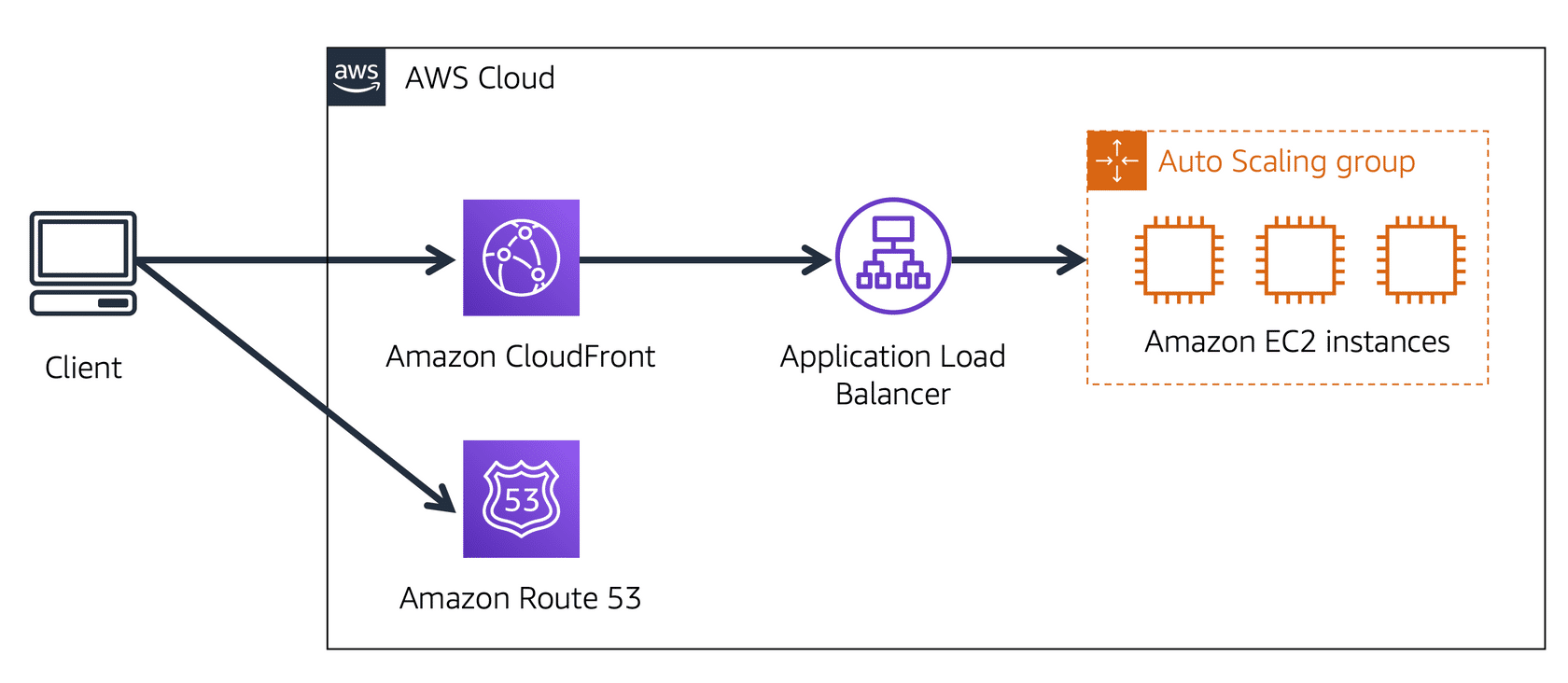
Image created by Amazon Web Services
The picture explained:
The company has 3 EC2 Instances in an Auto Scaling group.
The group is attached to an Application Load Balancer.
- User requests data from the website application.
- Route 53 uses DNS resolution to identify the IP address.
- The data is sent back to the user.
- The user request is sent to the nearest Edge Location through CloudFront.
- CloudFront connects to the Application Load Balancer.
- The Load Balancer sends the packet to the EC2 instance.
Related reads:


