JavaScript Math.cos()
Examples
let x = Math.cos(3.14);
Try it Yourself »
Math.cos(0);
Math.cos(Math.PI);
Math.cos(2 * Math.PI);
Try it Yourself »
Math.cos(x) expects x radians.
To use degrees, convert the degrees to radians.
Math.cos(degree * Math.PI / 180);
Try it Yourself »
Definition and Usage
The Math.cos() method returns the cosine of a number.
The Math.cos() method returns a number between -1 and 1.
The Math.cos() method expects the number in radians.
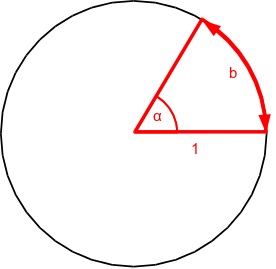
What is Radians?
Radians is an angle's α amount of rotation b on a circle:
| Degrees | PI | Radians |
|---|---|---|
| 0° | 0 | 0 |
| 1° | PI/180 | 0.0175 |
| 30° | PI/6 | 0.52 |
| 45° | PI/4 | 0.79 |
| 90° | PI/2 | 1.57 |
| 180° | PI | 3.14 |
| 360° | PI*2 | 6.28 |
JavaScript Sine and Cosine Methods:
The Math.sin() MethodThe Math.sinh() Method
The Math.asin() Method
The Math.asinh() Method
The Math.cos() Method
The Math.cosh() Method
The Math.acos() Method
The Math.acosh() Method
Syntax
Math.cos(x)
Parameter
| Parameter | Description |
| x | Required. A number representing radians. |
Return Value
| Type | Description |
| Number | -1 to 1 The cosine of the number.NaN if the parameter is not numeric. |
The Pythagoran Therorem
Math.sin(), Math.cos(),
and Math.tan() are related to the Pythagorean theorem:
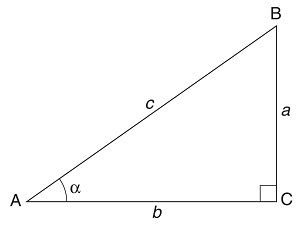
Theorem: c2 = a2 = b2
The sine Math.sin() to the angle is a / c.
The cosine Math.cos() to the angle is b / c.
The tangent Math.tan() to the angle is a / b.
Browser Support
Math.cos() is an ECMAScript1 (ES1) feature.
ES1 (JavaScript 1997) is fully supported in all browsers:
| Chrome | Edge | Firefox | Safari | Opera | IE |
| Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes |


